Introduction to Computer Networking: The Basics You Need to Know 🌐✨
In today’s hyper-connected digital world, computer networking forms the backbone of nearly every online activity. Whether you’re sending emails, streaming videos, or collaborating with colleagues across the globe, networks make these interactions possible. But what exactly is a computer network, and why is it so critical to modern life?
In this post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of computer networking and break down key concepts that help keep our digital world running smoothly.
What is a Computer Network? 💻
A computer network is essentially a collection of interconnected devices—such as computers, servers, routers, and switches—that communicate with one another to share data, resources, and services. These devices, often referred to as “nodes,” can connect through physical cables (in a wired network) or via wireless signals (such as Wi-Fi). Regardless of the connection type, the purpose remains the same: facilitating communication and data exchange between devices.
Networks can range in size and complexity, from small setups like a home Wi-Fi network to vast, sprawling infrastructures like the internet.
Why is Networking Important?
Simply put, without networks, much of what we rely on in today’s world would cease to function. The internet, the largest and most well-known network, depends on interconnected systems to provide services like web browsing, cloud computing, online shopping, social media, and more.
Beyond personal use, networks are crucial for businesses, governments, educational institutions, and healthcare systems. They support everything from communication and collaboration to data storage and security. Without reliable networks, operations in nearly every sector would grind to a halt.
Common Types of Computer Networks 🛠️
Understanding different types of networks is key to grasping how information travels and how various systems are connected. Let’s break down the most common network types: 
1. LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as an office, home, or small campus. It’s typically confined to a single building or close proximity, making it ideal for sharing resources like printers or files within a localized environment. Think of the Wi-Fi network at your home or in a coffee shop as an example of a LAN. 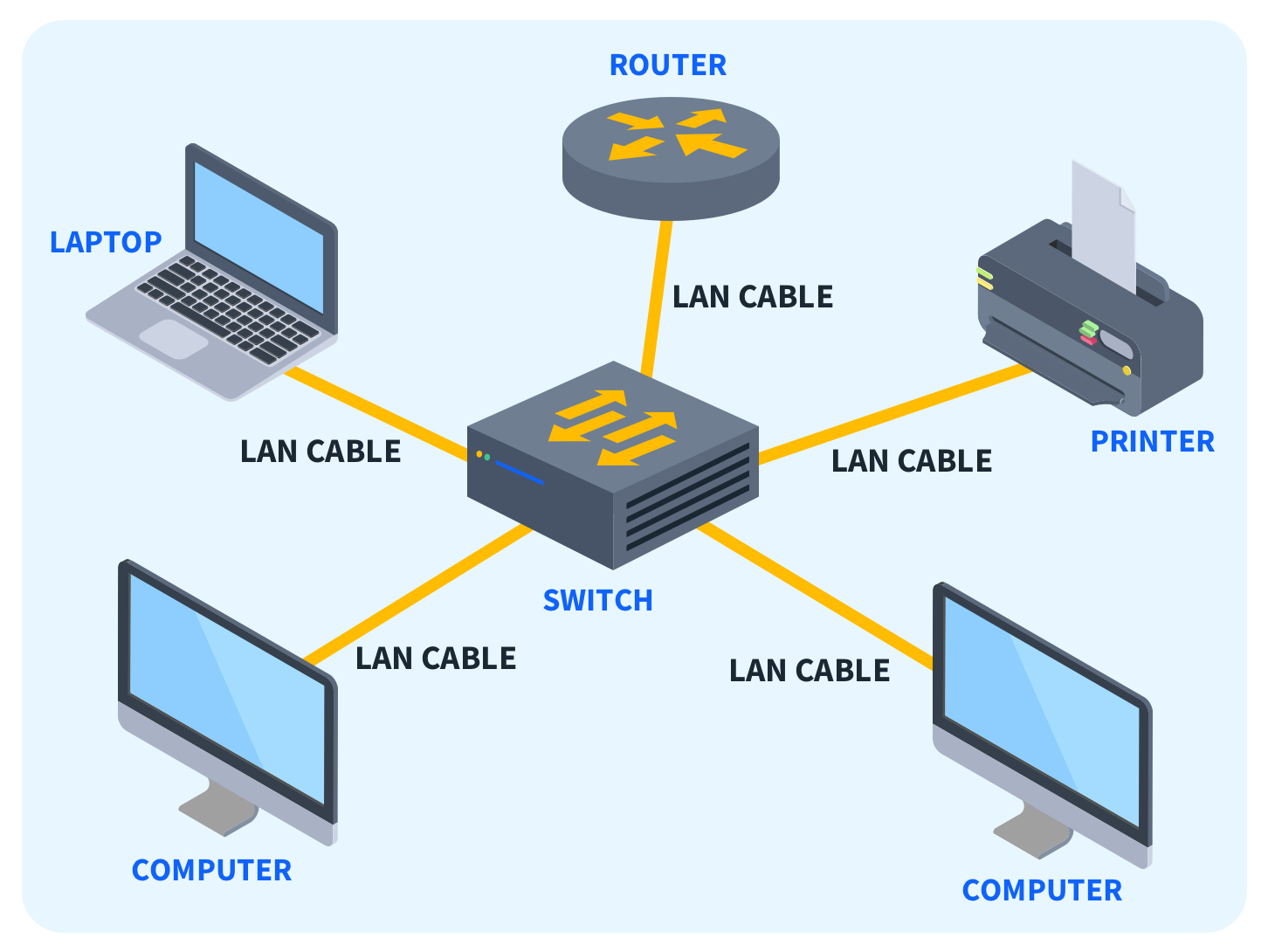
2. WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN, as the name suggests, covers a much larger geographical area—this can be across cities, countries, or even continents. The internet is the largest example of a WAN, connecting millions of smaller networks (such as LANs and MANs) around the globe. WANs enable long-distance communication and are crucial for connecting users in different locations. 
3. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
Sitting somewhere between a LAN and a WAN in terms of size, a MAN spans a city or a large campus. It is designed to cover larger areas than a LAN but without the global reach of a WAN. For instance, universities or city governments might use a MAN to interconnect various facilities and departments within a metropolitan area.
4. PAN (Personal Area Network)
A PAN is essentially a network that centers around an individual’s personal devices, like your smartphone, laptop, smartwatch, or Bluetooth headphones. It’s a small-scale network designed to connect your devices for easy file sharing or communication, often through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. PANs are increasingly important as our lives become more connected with smart devices and IoT (Internet of Things) technology.
How Do Networks Work?
At the heart of any network are protocols—rules and standards that dictate how data is transmitted and received. One of the most well-known is the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which governs communication over the internet. Devices on a network must follow these protocols to ensure that data travels to its intended destination securely and efficiently.
Additionally, every device connected to a network has an IP (Internet Protocol) address, which functions like a digital mailing address. It allows data packets to be sent from one device to another, ensuring they reach the correct location. Routers and switches direct these packets through the network, ensuring smooth communication between devices.
The Role of Networking in Modern Technology
The importance of networking continues to grow as technology evolves. From cloud computing and the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) to remote work and virtual collaboration, networks play a pivotal role in shaping the future. In cybersecurity, for instance, network security is critical to protect sensitive data from threats and ensure privacy. In business, reliable networks can enhance productivity by enabling seamless communication and access to shared resources.
Moreover, advancements in networking technologies, like 5G and Wi-Fi 6, are further pushing the boundaries of speed, connectivity, and efficiency, paving the way for innovations such as smart cities and autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
Computer networking is the invisible force powering much of our modern digital world. From personal devices to global enterprises, the ability to connect and communicate efficiently is what keeps our society functioning. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a professional in the field, or just curious about how things work, understanding the basics of computer networking is essential in navigating today’s digital landscape.
By learning about the different types of networks, how they function, and their role in modern technology, you’ll have a solid foundation to explore more advanced concepts and applications in this fascinating field.
